Certification & Quality Approvals
Meeting certifications specific to different industries
Certified to perform in even the harshest environments
UTimages promotes standardization of material, facilities, and engineering practices to improve industrial safety standards and regulations, while reducing the total cost of ownership and acquisition cycle time.
With our manufacturers and vendors, we implement their quality management system based on a process management approach. This allows us to maintain consistency in product service and support, and meet all applicable regulatory requirements. The quality system complies with the international standard ISO 9001:20015 and the standards which apply to related industries.
Below are the standards we offer and thus require from our contracted manufacturing facilities:
MIL-STD810G
The MIL-STD-810G test series are approved for use by all departments and agencies of the United States Department of Defense (DoD). MIL-STD-810G addresses a broad range of environmental conditions that include: low pressure for altitude testing; exposure to high and low temperatures plus temperature shock (both operating and in storage); rain (including wind blown and freezing rain); humidity, fungus, salt fog for rust testing; sand and dust exposure; explosive atmosphere; leakage; acceleration; shock and transport shock; gunfire vibration; and random vibration. The standard describes environmental management and engineering processes that can be of enormous value to generate confidence in the environmental worthiness and overall durability of a system design.
| MIL-STD-810G Method 501.4 | High Temperature |
| MIL-STD-810G Method 502.4 | Low Temperature |
| MIL-STD-810G Method 506.4 | Rain / Water Resistance |
| MIL-STD-810G Method 507.4 | Humidity |
| MIL-STD-810G Method 514.5 | Vibration |
| MIL-STD-810G Method 516.5 | Shock |
| MIL-STD-810G Method 503.4 | Temperature Shock |
| MIL-STD-810G Method 500.4 | Low Pressure |
MIL-STD-461F
MIL-STD-461 is a United States Military Standard that describes how to test equipment for electromagnetic compatibility. Specifically, MIL-STD 461F details testing specification to ensure the conducted emissions (CE), conducted susceptibility (CS), radiated emissions (RE), and radiated susceptibility (RS) of a system can meet the requirements for the control of electromagnetic interference.
| MIL-STD-461 Method - CE101 / CE102 | Conducted Emissions |
| MIL-STD-461 Method - CS101 / CS106 / CS109 / CS114 / CS115 / CS116 | Conducted Susceptibility |
| MIL-STD-461 Method - RS101/RS103 | Radiated Susceptibility |
| MIL-STD-461 Method - RE101 / RE102 | Radiated Emissions |
EN50155
The EN50155 standard is a guidebook that governs the design and testing of electronic equipment used on railway vehicles and related rail applications. To meet the EN50155 requirement, the components must go through a series of strict tests including EMC, cooling, damp heat, salt mist, vibration, and shock tests.
|
|
||
| Cooling | EN50155:2001 / 10.2.3 EN60068-2-1, Test Ad |
||
| Dry Heat (operation) | EN50155:2001 / 10.2.4 EN60068-2-2, test Bd |
||
| Damp heat test, cyclic | EN50155:2001 / 10.2.5 EN60068-2-30, Test Db |
||
| Salt Mist Test | EN50155:2001 / 10.2.10 | ||
| Vibration Test | EN50155:2001/10.2.11 EN61373 / IEC61373 / Section 8 ,Section 9 |
||
| Shock Test | EN50155:2001/10.2.11 EN61373 / IEC61373 / Section 10 |
||
| Low temp. storage test | EN50155:2001/10.2.14 EN60068-2-1 |
||
| Watertightness Test | EN50155:2001/10.2.12 EN60529 (IEC 60529) |
EN61373
This International Standard specifies the requirements for testing equipment for railway vehicles which are subjected to vibrations and shock. To ensure the operation of the equipment, it has to withstand tests of reasonable duration to simulate the service condition throughout its expected life.
Simulated long-life testing is achieved by amplification, where amplitudes are increased and the time base decreased.
Test carried out on Equipment using test values for Category 1 Body Mounted, Class B, which is defined as anything mounted inside an equipment case which is turn mounted directly on or under the car body.
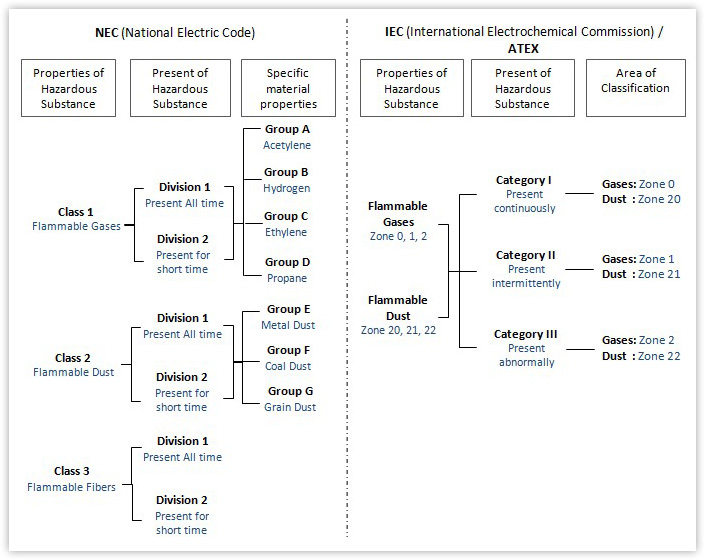
Class 1 Division 2 Group A-D and ATEX
Contract Facilities have addressed the Request for Panel PC equipment that can withstand Hazardous Location (Hazloc), where flammable substance may be present with C1D2 (for US and Canada market) and ATEX (for European market) certification on 15-inch Stainless Panel PC. In the US market we follow NEC, which place Hazloc into classes, divisions, and groups. For the rest of the market, IEC Classifies Hazloc by zones.
| NEC (National Electric Code) |
According to OSHA, NEC defines hazardous locations as those areas where fire or explosion hazards may exist due to flammable gases or vapors, flammable liquids, combustible dust of ignitable fibers or flyings. NEC classified Hazardous locations in three ways; Type, Condition, and Nature. |
| IEC (International Electrochemical Commission) |
IEC Defines the flammable gases and vapors and then flammable dust, each of this type are assigned into three different zone and each zone then requires equipment built for category I,II or III |
This following figure will help users catch a basic understanding on both classifications
The 15" Stainless Steel Panel PC has passed various tests and certifications for Hazardous area deployment
| America | Europe |
| Grade Class 1 Division 2, Group A,B,C,D, T4 |
Grade II 3 G Ex nA ic IIA T4 II 3 G Ex nA ic IIA T4 |
| Certification ISA 12.12.01-2012 CSA C22.2 No.213-M1987 CSA 22.2 No. 60950-1-07 FCC |
Certification ATEX 94/9/EC UL 60950-1 CE |
| Test Report IEC 60079-11 , Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "I" IEC 60079-15, Equipment protection by type of protection "n" |

DNV 2.4, IEC60945, IACS-E10
Marine products are built and tested according to DNV standard certification 2.4, IEC60945, and IACS-E10 and most of the products are certified by Det Norske Veritas (DNV), the Norwegian foundation internationally certifying materials, components and system relevant to safe operation and quality of ships.
| DNV 2.4 | DET NORSKE VERITAS (DNV) is an autonomous and independent foundation with the objectives of safeguarding life, property and the environment at sea and on shore. DNV certification related to quality of ships, offshore units and installations of the system and components. DNV Requirements are harmonized with IACS Unified Requirements E10 and IEC publication 60945. |
| IACS-E10 | International Association of Classification Societies (IACS) is an organization that provides technical support and guidance for promoting the safety of life, property and the environment through the verification of compliance with technical and engineering standards for the design, construction and life-cycle maintenance of ships, offshore units and other marine-related facilities |
| IEC 60945 | Equipment wished to be use in navigation and radio communication systems is to comply with IEC Publication No. 60945, "Maritime navigation and radio communication equipment and systems – General Requirements- Method of testing and required test results" |
Standard for Certification
DNV classifies tests in four levels base on the product applied location in ships-A, B, C, and D. For worse harsh environment use, the much strict standard testing is required. (See Table of Location Classes Selection Guide) Standards for Certification including contain principles, acceptance criteria and practical information related to the Society's consideration of objects, personnel, organizations, services and operations. A list of Standards for Certification is found in the latest edition of Pt.0 Ch.1 of the "Rules for Classification of Ships" and the "Rules for Classification of High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface Craft".
| Column I | Column II | |||||
|
Parameters
|
Location within main area
|
Main Areas On Board | ||||
| Machinery spaces | Control Room, Acc. | Bridge | Pump room, Holds, Rooms with no heating | Open deck | ||
|
Temperature
|
Inside cubicles, desks, with temp rise 5oC or more | B | B | B | D | D |
| All other locations | A | A | A | C | D | |
|
Humidity
|
Locations where special precautions are taken to avoid condensation | A | A | A | A | A |
| All other locations | B | B | B | B | B | |
|
Vibration
|
On Machinery such as internal combustion engines, compressors, pumps, including piping on such machinery | B | - | - | B | B |
| Masts | - | - | - | - | C | |
| All other locations | A | A | A | A | A | |
| EMC | All locations within specified main areas | A | A | B | A | B |
|
Enclosure
|
Submerged application | D | - | - | D | D |
| Below floor plates in engine room | C | - | - | - | - | |
| All other locations | B | A | A | B | C | |
IEC 61850-3
IEC 61850-3 is a standard that outlines a comprehensive safety framework for substation automation, transmission & delivery (T&D) automation, and smart grid application. The standard emphasizes the EMI immunity and environmental requirements for communications networks. The product that meets the IEC 61850-3 standard provides full-range, redundant power supply which ensures the high quality of electricity transmission.
The equipment that meets the IEC 61850-3 requirement have the following characteristics:
| Reliability | Substation automation system (SAS) will keep operating when single communication component breaks down. |
| Availability | The equipment provides system and data backup and avoids impacts from system failover. |
| Maintainability | Well trained technicians will provide on-line and on-site maintenance service. |
| Safety | The equipment could keep the system from potential risks and instability. |
| Data Integrity | The system will keep the false data at certain levels to meet the I1, I2, or I3 standard. |
ISO 13485
ISO 13485 is an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard, published in 2003, a quality management system standard specifically for the medical devices industry. It was written to support medical device manufacturers indesigning quality management systems that establish and maintain the effectiveness of their processes. It ensures the consistent design,development, production, installation, and delivery of medical devices that are safe for their intended purpose.

Quality Systems
UTimages developed and implemented, with our partners, a quality management system to provide consistent products that meet customer and applicable regulatory requirements. Customer satisfaction is kept through the continual improvement and the prevention of non-conformity.

